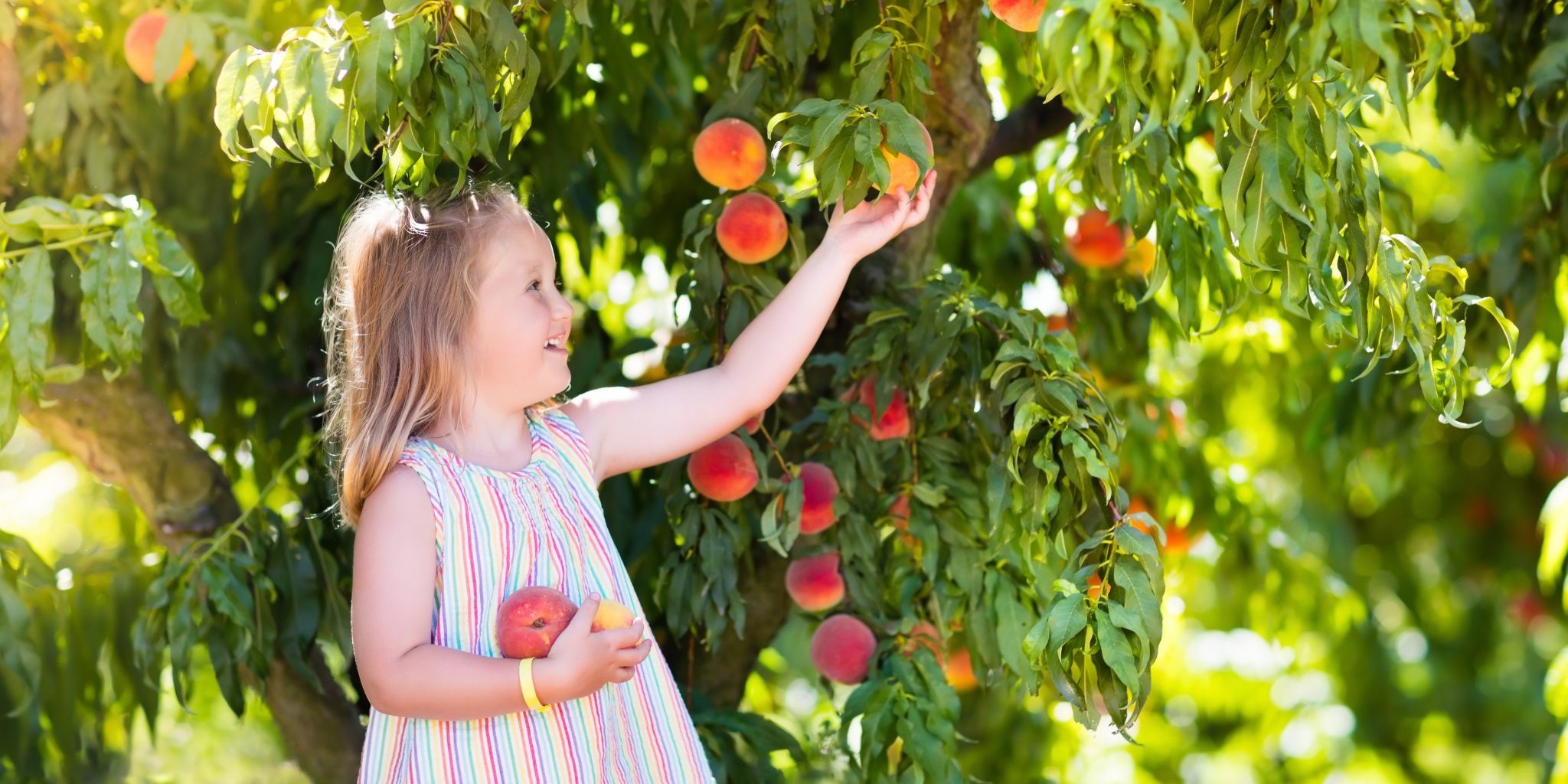
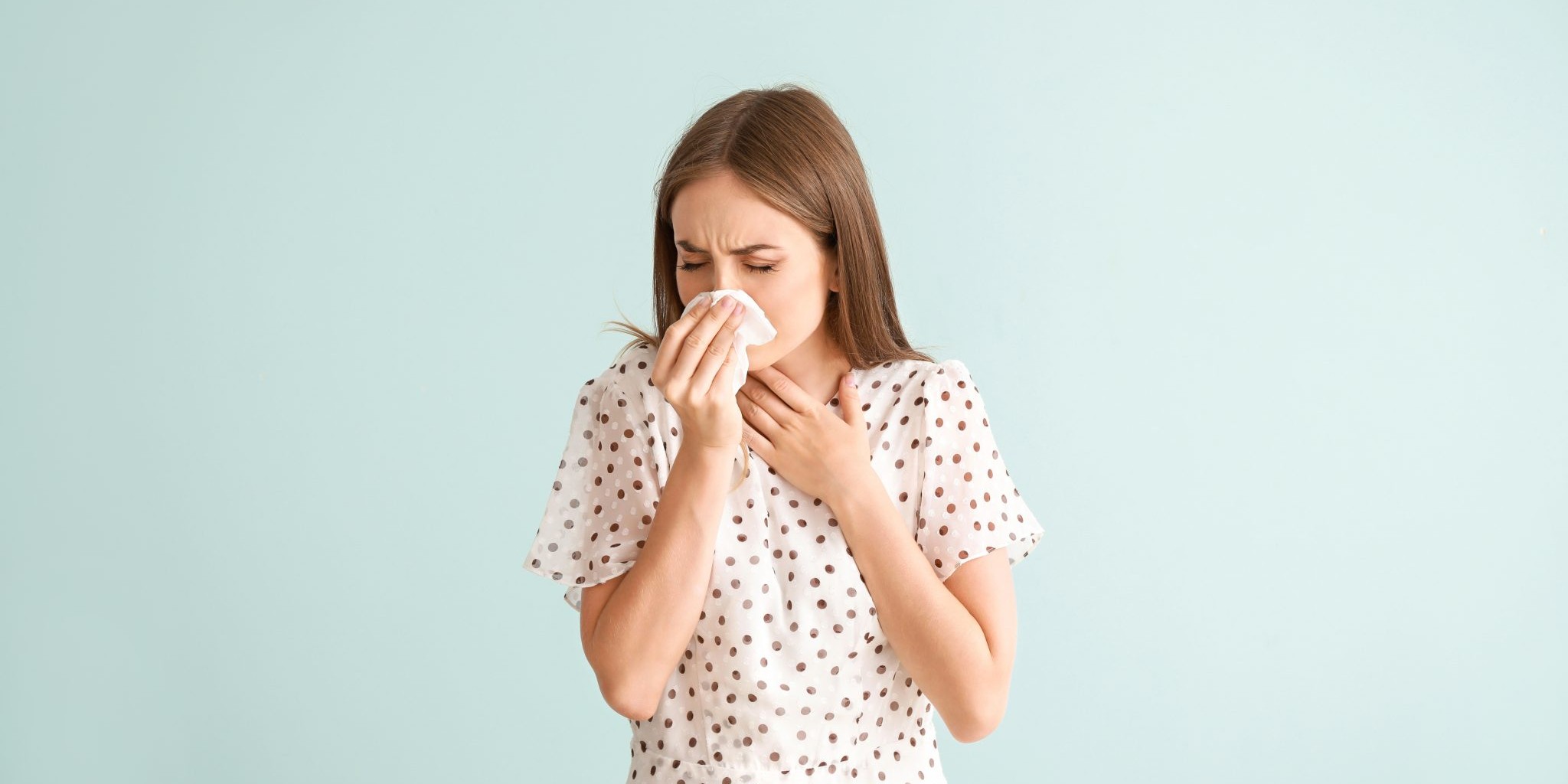
Oral Allergy Syndrome
June 9, 2022
Delicious, ripe, mouthwatering fruits and vegetables are more plentiful during these summer months. However, that that summer breeze may carry more than just excitement for the season. Some people with environmental allergies may notice that certain fruits, vegetables, or nuts give them distinct…
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
May 23, 2022
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a recognized diagnosis that produces symptoms related to dysfunction of the esophagus. In EoE, large amounts of white blood cells, specifically eosinophils, collect in the inner lining of the esophagus resulting in inflammation. Typically, the esophagus is free…
Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis
November 29, 2021
We have made it to the highly anticipated holiday season! We ate more than our share of turkey, taken down the last of the fall décor, have started trimming the tree, and are double down on the holiday gift lists. With winter weather upon us or in the near future, and personal care products a…
Skin Care Tips: Atopic Dermatitis & Eczema
February 22, 2021
From Amanda Hofmann, VP Clinical at United Allergy Services: Earlier this month, the famous groundhog, “Punxsutawney Phil”, saw his shadow and promised 6 more weeks of winter. This past week, Phil showed he was serious about that promise as winter storms swept across most of the US. This recent…
Immunotherapy for Atopic Dermatitis
July 11, 2012
Atopic dermatitis is often the first symptom of allergic disease, commonly affecting young children, typically before 5 years of age. Atopic dermatitis is triggered by allergies to foods and environmental allergens (such as pollen, molds, pet dander and dust mites) in 85 percent of affected people.…